What is Certificate Transparency?
A brief on certificate transparency, an open standard to detect malicious digital certificates.
In July 2011, DigiNotar, a Dutch Certificate Authority (CA) was compromised by unknown attackers, and rogue certificates were issued for several domains. These malicious certificates were then used for man-in-the-middle attacks to spy on unsuspecting victims. While DigiNotar couldn't survive this and went bankrupt, the breach ironically spurred the industry into action and had a lasting impact on the security of public web trust infrastructure.
Lack of transparency into certificate issuance was the biggest takeaway from the DigiNotar incident - they had no idea (and logs) that malicious certificates were issued on their behalf. While CAs and web browsers have since streamlined the verification process using automated validity checks, certificate pinning and other mechanisms, the biggest effort to come out of this is certificate transparency.
Certificate Transparency (CT) is an open security standard that helps detect and protect against malicious digital certificates. The standard creates a ledger of public, tamper-proof, append-only logs for all certificates issued by trusted CAs. Some browsers like Chrome and Safari require certificates to show proof of being logged onto the ledger. This is done using a signed certificate timestamp embedded inside the certificate or via a TLS extension. CT uses a cryptographic mechanism called Merkle trees to prevent entries from being modified or deleted. Google was the first company to launch a CT log back in 2015, but others have followed suit since, most notably Cloudflare (Nimbus) and Let's Encrypt (Oak).
The Certificate Transparency Project is an ecosystem of several important and supportive partners, who collectively help to secure communication on the internet. Over 6.5 billion certificates have been logged since 2013, with the ledger offering a treasure trove to anyone wishing to monitor and analyse the logs.
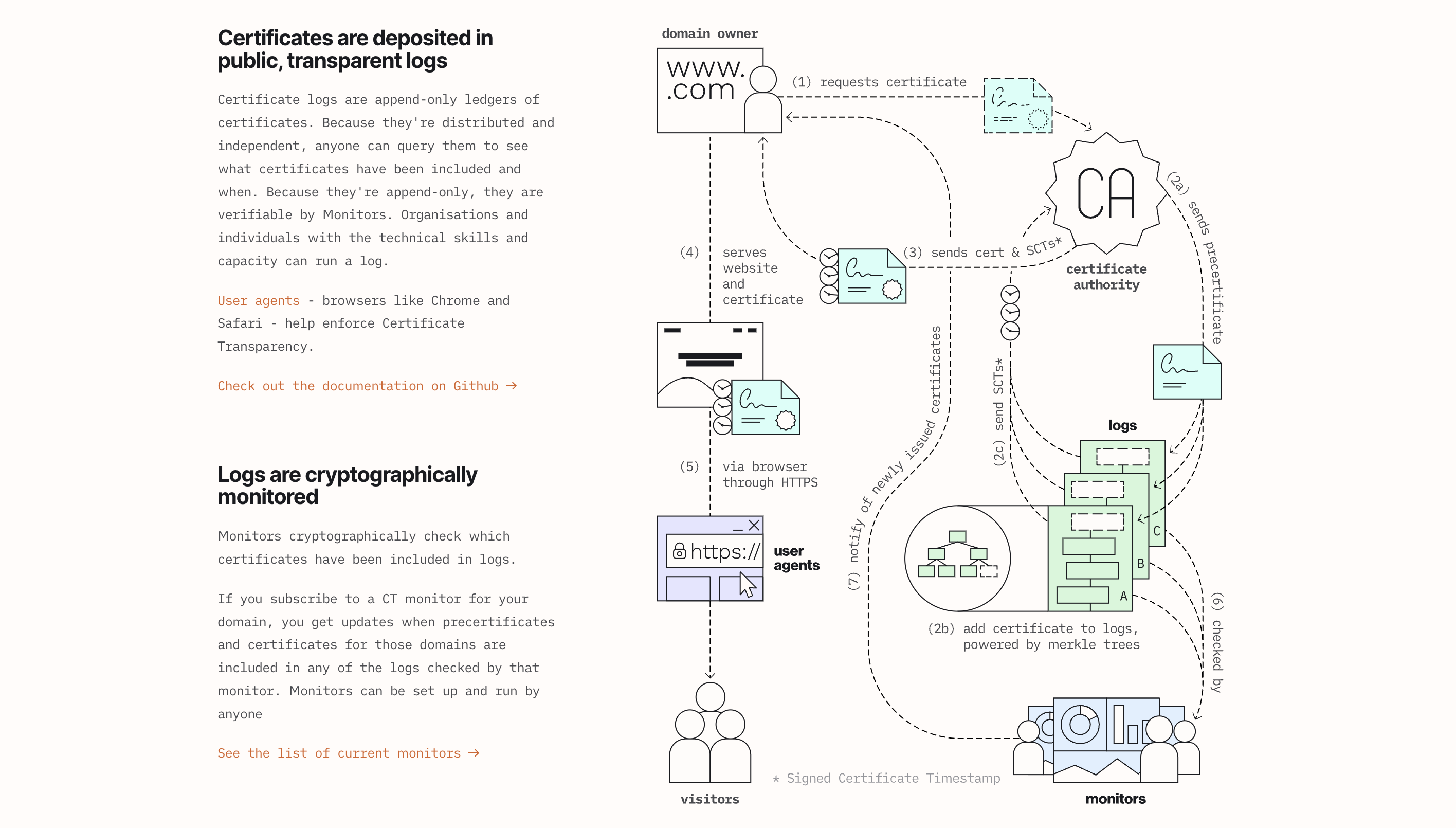
If you are keen to understand how CT works behind the scenes, have a look at the detailed post here. An excerpt is shown below.
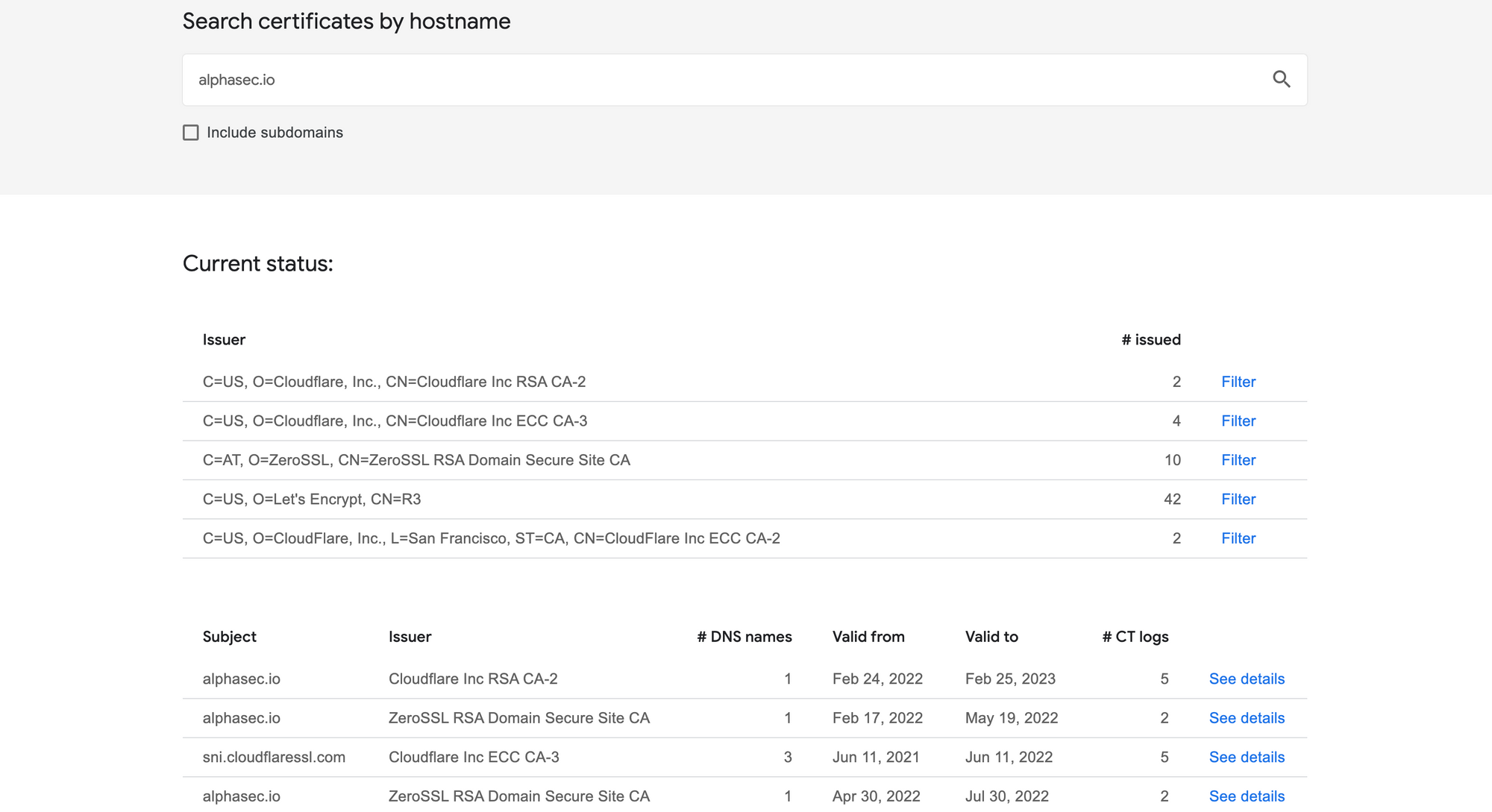
Various sites like Google, Facebook, Cloudflare and others offer the ability to lookup all of a domain's certificates present in active public CT logs. CT monitors are run by organisations to periodically audit the log servers and watch for suspicious activity. Here is a sample search result for alphasec.io using Google.
Certificates are foundational to the web public key infrastructure, which in turn ensures security for all digital communications, and CT brings much needed transparency to the entire ecosystem.